Initializtion Function
內容表格
沒有標頭A RAID controller enables RAID by logically linking multiple HDD units. All the HDD units that are used for constructing RAID are not necessarily new or data in the HDD units have not necessarily been deleted. The initialization function performs initialization processing for the HDD units that are used for constructing RAID. Three types of RAID controller initialization are available, normal initialization (NI), fast initialization (FI), and background initialization (BGI).
Normal initialization and fast initialization
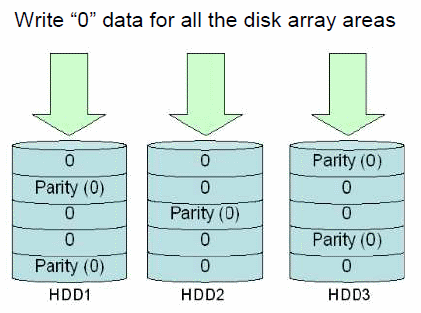
In normal initialization, zero data is written to all the HDD areas that configure the disk array. Since the information in the HDD is cleared to 0, the entire invalid data that has been originally stored in the HDD can be deleted. Since all zero data is recorded, the consistency of the parity information is also restored.
Fast initialization (FI)

In fast initialization, zero data is written only in the top sections of the HDD units that form the disk array. The OS install information and partition information can be cleared. Since shorter processing than normal initialization is required, processing can be advanced to the next task quickly. However, as some areas are not initialized, consistency of all the disk array areas is not established.
Background initialization (BGI)

When fast initialization is executed, normal initialization is interrupted, or initialization is not executed for the disk array, the disk array contains uninitialized areas. Background initialization is the function that matches the parities for all the uninitialized areas in background.
