Write Cache Function
內容表格
沒有標頭Cache is the memory that is installed in a RAID controller and is used as a data buffer for the RAID controller
to read and write data to the HDD units. Cache is used as a work area for parity generation processing.
Write Through
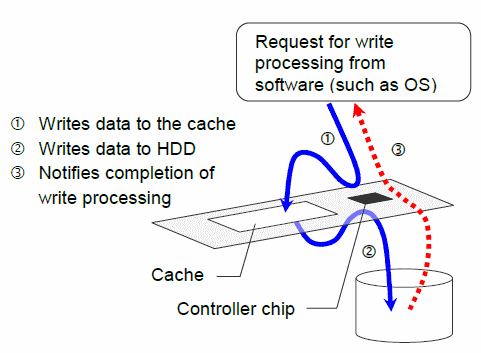
When write processing is requested from software such as OS, data is written to both the cache and the HDD on the RAID controller in Write Through mode. Since software advances to the next processing after completion of HDD write processing, in general, the
access performance deteriorates due to Write Back. However, since the write request from the software reflects in the HDD immediately, the advantage of this mode is the low risk of losing data at the occurrence of an unexpected accident such as a temporary power failure.
Write Back
When write processing is requested from software such as OS, in Write Back mode, data is written to the cache in the RAID controller and to the HDD by the RAID controller asynchronously based on the data on the cache.
Since completion notification is issued to the software when data is written to the cache, the software can continue processing without having to wait for completion of the HDD write processing.
In general, access performance is improved by Write Through. However, since the contents of the cache may not reflect in the HDD at the occurrence of an unexpected accident such as a temporary power failure, the data may be lost.
