網路指令與技巧
Tutorials
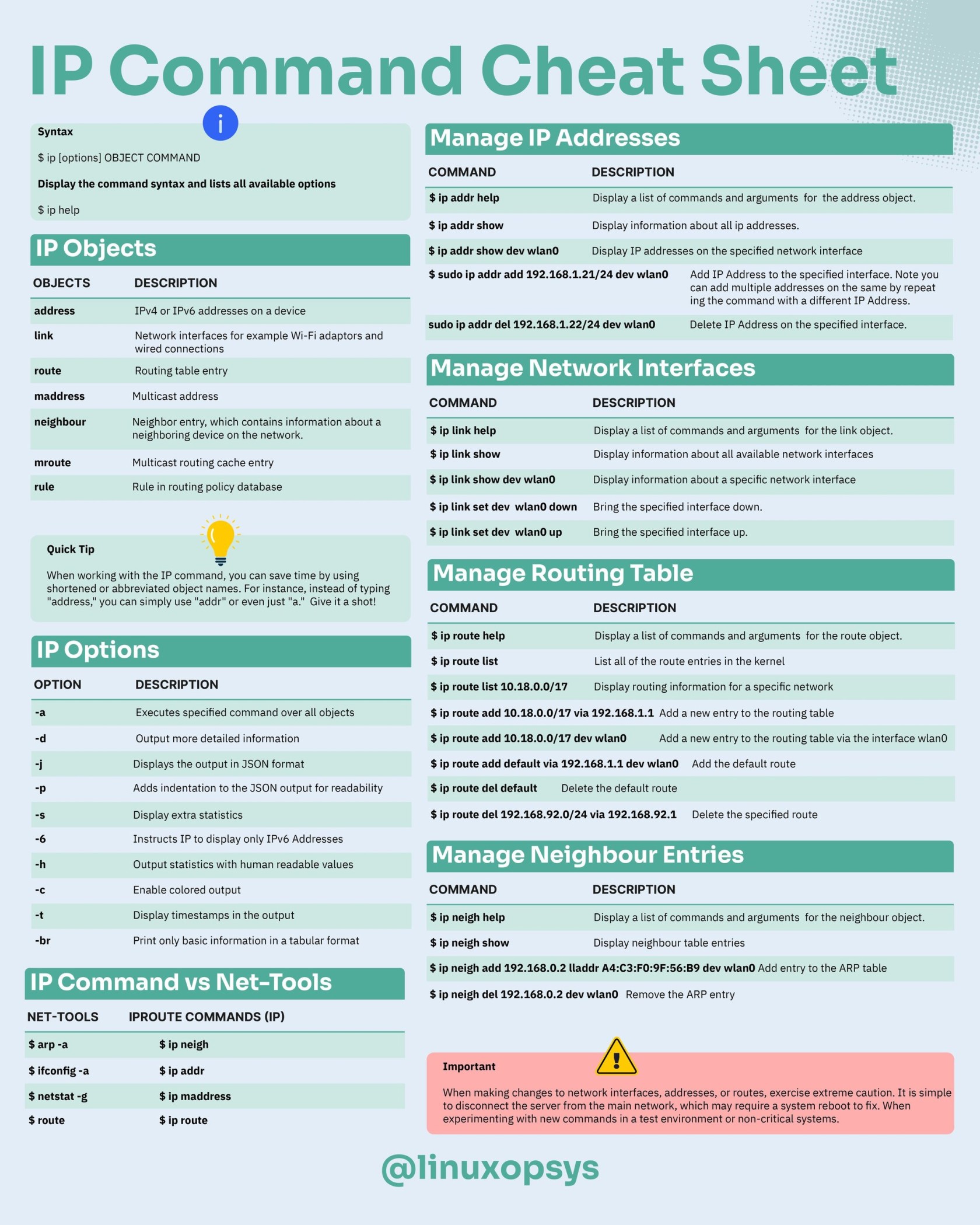
ip
# 顯示所有網卡資訊
ip addr
ip a
# 顯示所有網卡的 IP
ip -br -c addr show # 需要較新版 ip
# 顯示 eth0 網卡資訊
ip a show eth0
# 開啟/關閉網卡
ip link set eth0 { up | down }
# 顯示所有的網路裝置
ip link show
ip -br -c link show
ip l show
# 設定 IP (非永久)
ip a add 192.168.1.200/255.255.255.0 dev eth0
# 移除 IP (非永久)
ip a del 192.168.1.200/255.255.255.0 dev eth0
# 顯示 default gateway 及路由表
ip route show
ip r show
ip route add 10.10.20.0/24 via 192.168.50.100 dev eth0
ip route del 10.10.20.0/24
# Default gateway
ip route add default via 192.168.50.100
# 網路即時狀態
ip -s link
# 顯示 ARP 紀錄 (NOTE: 查詢連接網路設備的 MAC address 與 IP 對應表)
ip neigh show
ip n show
# 清除 ARP 清單裡的某個 IP 紀錄
ip -s -s n f <ip-address>
# 線上求助
ip a help在多個網路埠的主機上,如何得知哪些埠有接上網路線
# 1. 列出所有網路埠
ip link show 如果埠號顯示 DOWN 必須先啟動
# 2. 啟動網路埠 NOTE: 啟動前要注意 IP 是否會衝突
ip link set eth6 up
# 3. 啟動後檢測線路
ethtool eth6 | grep detectedCheat Sheet
nmcli
# List all of ethernet devices
nmcli con show
nmcli con show <conn-name>
nmcli dev status
# see only the active connections
nmcli con show -a
# Restart the network adapter enp0s3
nmcli con down enp0s3 && nmcli con up enp0s3
# Configure the static ip
nmcli con mod enp0s3 ipv4.addresses 192.168.20.170/24
nmcli con mod enp0s3 ipv4.gateway 192.168.20.1
nmcli con mod enp0s3 ipv4.method manual
nmcli con mod enp0s3 ipv4.dns "8.8.8.8"
nmcli con down enp0s3
nmcli con up enp0s3
# make a new ethernet connection with name Myhome1, assigned to device enp0s3
nmcli con add type ethernet con-name Myhome1 ifname enp0s3 ip4 192.168.1.50/24 gw4 192.168.1.1
cat /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-Myhome1GUI to Configure Network
# For Ubuntu/Debian
sudo apt install network-manager
# Console Command
nmtuinetplan
Recommended on Ubuntu/Debian
- A declarative approach to Linux networking with Netplan | Ubuntu
- Netplan brings consistent network configuration across Desktop, Server, Cloud and IoT | Ubuntu
sudo vi /etc/netplan/01-network-manager-all.yaml
network:
version: 2
renderer: networkd
ethernets:
ens18:
dhcp4: no
addresses:
- 192.168.1.22/24
gateway4: 192.168.1.101
nameservers:
addresses: [8.8.8.8, 8.8.4.4]Commands
# Validate Configuration File
sudo netplan try
# Apply the Configuration
sudo netplan apply
# Check the network stack
sudo netplan status
# Optional: Restart the Network Service
sudo systemctl restart systemd-networkdethtool
# ethtool ens192
Settings for ens192:
Supported ports: [ TP ]
Supported link modes: 1000baseT/Full
10000baseT/Full
Supported pause frame use: No
Supports auto-negotiation: No
Supported FEC modes: Not reported
Advertised link modes: Not reported
Advertised pause frame use: No
Advertised auto-negotiation: No
Advertised FEC modes: Not reported
Speed: 10000Mb/s
Duplex: Full
Port: Twisted Pair
PHYAD: 0
Transceiver: internal
Auto-negotiation: off
MDI-X: Unknown
Supports Wake-on: uag
Wake-on: d
Link detected: yes# ethtool -i ens192
driver: vmxnet3
version: 1.4.17.0-k-NAPI
firmware-version:
expansion-rom-version:
bus-info: 0000:0b:00.0
supports-statistics: yes
supports-test: no
supports-eeprom-access: no
supports-register-dump: yes
supports-priv-flags: no# ethtool -S ens192
NIC statistics:
Tx Queue#: 0
TSO pkts tx: 540499
TSO bytes tx: 28911908774
ucast pkts tx: 10060867
ucast bytes tx: 29602317140
mcast pkts tx: 0
mcast bytes tx: 0
bcast pkts tx: 5655
bcast bytes tx: 237510
pkts tx err: 0
pkts tx discard: 0
drv dropped tx total: 0
too many frags: 0
giant hdr: 0
hdr err: 0
tso: 0
ring full: 0
pkts linearized: 0
hdr cloned: 0
giant hdr: 0
Tx Queue#: 1
TSO pkts tx: 317
TSO bytes tx: 599134
ucast pkts tx: 1702836
ucast bytes tx: 101410145mii-tool
# Installation
sudo apt install net-tools
# CHECK A SINGLE INTERFACE
sudo mii-tool <interface_name>
# SEE DETAILED INFORMATION
sudo mii-tool -v <interface_name>
# SET NETWORK INTERFACE SPEED
sudo mii-tool –force 10baseT-FD <interface_name>
# RESTART AUTO-NEGOTIATION
# Network devices use an auto-negotiation protocol to communicate the technologies they support.
# It will then select the fastest mutually supported technology.
# To restart the auto-negotiation of the interface, run the following command.
sudo mii-tool –restart <interface_name>
# CHANGE THE DUPLEX MODE
# For example, here I have set the speed of the eth0 interface to 10 Mbps and the duplex mode to half-duplex.
sudo mii-tool -F 10baseT-HD eth0
# REPORT LINK STATUS CHANGES
# Run the following command to watch a single interface and report changes in the link status.
# That is to say, the interfaces are listed at one second intervals by default.
sudo mii-tool -w <interface>
# REPORT LINK STATUS
sudo mii-tool -l <interface_name>
# RESET THE CONFIGURATIONS
# Most importantly, you should be able to reset it to its default configuration
# if something goes wrong. For that, run the following command
sudo mii-tool -R <Interface_name>systemctl
# Bringing UP/Down Network Interface
systemctl restart network
# or
systemctl restart network.servicespeedtest CLI
# Ubuntu/Debian
curl -s https://install.speedtest.net/app/cli/install.deb.sh | sudo bash
sudo apt-get install speedtest
# CentOS/RedHat
curl -s https://install.speedtest.net/app/cli/install.rpm.sh | sudo bash
sudo yum install speedtestState of Network Cable
# Device: enp5s0
# Output: 1 means Connected
cat /sys/class/net/enp5s0/carrier
# Output: Up means Connected
cat /sys/class/net/enp5s0/operstate
# Using ethtool
# Output: Link detected: yes
sudo ethtool enp5s0
# Using ip
# Output: state UP
ip a
Network Adapters
Modern Linux
lshw -class network -shortOld Linux
lspci | egrep -i --color 'network|ethernet'Disable IPv6
Ubuntu 20.04
sudo vi /etc/default/grub
# Change the line as follows
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="ipv6.disable=1"
# Update the GRUB
sudo update-grub
# Reboot
systemctl rebootDebian 10
/etc/sysctl.conf :
# Disable IPv6 on all network adapters
net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 = 1Apply the change :
sysctl -pRedHat 4
1. Remove the following line (if present) from the /etc/modprobe.conf file:
alias net-pf-10 ipv62. Add the following line to the /etc/modprobe.conf file:
alias net-pf-10 off3. Comment out any IPv6 addresses found in /etc/hosts, including ::1 localhost address
cp -p /etc/hosts /etc/hosts.disableipv6
sed -i 's/^[[:space:]]*::/#::/' /etc/hosts如果以上步驟仍無法關閉 IPv6,檢查是否有啟動 openibd 服務,將它關閉試試
openibd is a High Availability service for IPoIB (IP over InfiniBand) interface. The service loads the ib_ipoib module, which has a dependency on the ipv6 module
service openibd stop
chkconfig openibd off
rebootRedHat 5/6
/etc/sysctl.d/ipv6.conf :
# For v5/6
# IPv6 support in the kernel, set to 0 by default
# Disable IPv6
net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 = 1
net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6 = 1RedHat 7
/etc/sysctl.d/ipv6.conf :
# To disable for all interfaces
net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 = 1重建開機映像檔
如果沒有重建開機映像檔,會使得 rpcbind.service 無法正常運作,這會影響 NFS 的掛載。
RedHat 8
Create the file /etc/sysctl.d/ipv6.conf :
# First, disable for all interfaces
net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 = 1
# If using the sysctl method, the protocol must be disabled all specific interfaces as well.
#net.ipv6.conf.<interface>.disable_ipv6 = 1Reload sysctl :
sysctl -p /etc/sysctl.d/ipv6.confCreate a backup of the initramfs :
cp /boot/initramfs-$(uname -r).img /boot/initramfs-$(uname -r).bak.$(date +%m-%d-%H%M%S).imgRebuild the Initial RAM Disk Image :
dracut -f -vVerifying file inclusion :
lsinitrd /boot/initramfs-<version>.img | grep 'etc/sysctl.d/ipv6.conf'Comment out any IPv6 addresses found in /etc/hosts, including ::1 localhost address
cp -p /etc/hosts /etc/hosts.disableipv6
sed -i 's/^[[:space:]]*::/#::/' /etc/hostsWiFi Management
# Replace 'wlan0' with your wifi interface
sudo iwlist wlan0 scan | egrep "Cell|ESSID|Encryption|Quality"Block Attackers IP Address
Drop or Block Attackers IP Address With Null Routes On a Linux
# Using route command
route add 65.21.34.4 gw 127.0.0.1 lo
# veryfy it
netstat -nr
route -n
# Or
route add -host 64.1.2.3 reject
ip route get 64.1.2.3
# Using ip command
ip route add blackhole 202.54.5.2/29
ip route add blackhole 192.0.130.0/24
# verify it
ip route
# Removing null routing
route delete 65.21.34.4
# Or
route del -host 65.21.34.4 reject
# Or
ip route delete 1.2.3.4/26 dev eth0重設/移除不存在的網路裝置名稱
製作 Linux VM Template 時,每一次修改 Template 後都會產生新的編號作為網路裝置名稱。
然而透過這個 Template 新增的 Linux VM,系統的網路介面其實只有一個,不過裝置名稱可能已經編到 eth1 或 eth2 以後。正常來說,系統如果只有一個網路介面,網路裝置名稱通常為 eth0。
假使想要清除那些已經不存在的裝置名稱,或者讓系統對目前的網路裝置重新以 eth0 開始編號,步驟如下:
RedHat 6.x: 編輯 /etc/udev/rules.d/70-persistent-net.rules
# PCI device 0x15ad:0x07b0 (vmxnet3)
SUBSYSTEM=="net", ACTION=="add", DRIVERS=="?*", ATTR{address}=="00:50:56:83:7c:eb", ATTR{type}=="1", KERNEL=="eth*", NAME="eth0"
# PCI device 0x15ad:0x07b0 (vmxnet3) (custom name provided by external tool)
SUBSYSTEM=="net", ACTION=="add", DRIVERS=="?*", ATTR{address}=="00:50:56:83:7c:eb", ATTR{type}=="1", KERNEL=="eth*", NAME="eth1"註解或移除那些舊裝置名稱,只保留目前的裝置 eth1,然後將該行的 NAME 改成 eth0。
# PCI device 0x15ad:0x07b0 (vmxnet3) (custom name provided by external tool)
SUBSYSTEM=="net", ACTION=="add", DRIVERS=="?*", ATTR{address}=="00:50:56:83:7c:eb", ATTR{type}=="1", KERNEL=="eth*", NAME="eth0"存檔後重起 VM。
VM 啟動後,使用 setup 或 system-config-network 新增網路介面 eth0 的網路設定。
Disable WiFi
With nmcli
# nmcli dev status
DEVICE TYPE STATE CONNECTION
enp2s0 ethernet 已連線 enp2s0
wlp1s0 wifi 離線 --
lo loopback 不受管理 --
# nmcli radio wifi off
# nmcli dev status
DEVICE TYPE STATE CONNECTION
enp2s0 ethernet 已連線 enp2s0
wlp1s0 wifi 無法使用 --
lo loopback 不受管理 -- 查詢 DNS Server 位址
cat /etc/resolv.conf
nmcli dev show | grep -i dns
dig <domain-name>
resolvectl statusCustom MAC Address
RedHat 4
/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
DEVICE=eth0
ONBOOT=yes
BOOTPROTO=static
IPADDR=10.15.9.32
NETMASK=255.255.0.0
GATEWAY=10.15.8.254
#HWADDR=00:0C:29:B1:18:A3
MACADDR=00:0C:B1:B1:B1:B1
No Comments